In other words, is horizontal scaling or vertical scaling the right move for your business?
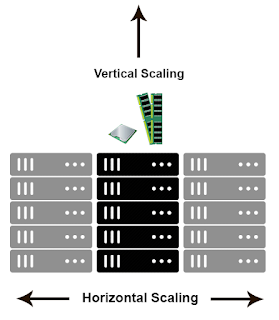
The heart of the difference is the approach to adding computing resources to your infrastructure. With vertical scaling (a.k.a. “scaling up”), you’re adding more power to your existing machine. In horizontal scaling (a.k.a. “scaling out”), you get the additional resources into your system by adding more machines to your network, sharing the processing and memory workload across multiple devices.
One way to look at it is to think of vertical scaling like retiring your Toyota and buying a Ferrari when you need more horsepower. With your super-fast car, you can fly at top speed with the windows down and look amazing. But, while Ferraris are awesome, they’re not very practical, they’re expensive, and at the end of the day, they can only take you so far before they’re out of gas. (Not to mention, there’s only two seats!)
Horizontal scaling gets you that added horsepower – not by ditching the Toyota for the Ferrari, but by adding another vehicle to the mix. In fact, you can think of horizontal scaling like several vehicles you can drive all at once. Maybe none of these machines is a Ferrari, but no one of them needs to be: across the fleet, you have all the horsepower you need.
Why Scaling Out Is Better Than Up
When you’re choosing between horizontal scaling and vertical scaling, you also have to consider what’s at stake when you scale up versus scale out.
In the Toyota-for-Ferrari trade-in scenario, you’re replacing a slower server with a bigger, faster one.
When you do this, though, you’re throttling yourself while the machine is taken offline for the upgrade. And, what happens down the road when your traffic is on the rise again and you have to repeat the upgrades? There are only a finite number of times you can go about solving your problem by “scaling up” in this manner.
Horizontal scaling is almost always more desirable than vertical scaling because you don’t get caught in a resource deficit. Instead of taking your server offline while you’re scaling up to a better one, horizontal scaling lets you keep your existing pool of computing resources online while adding more to what you already have. When your app is scaled horizontally, you have the benefit of elasticity.
You can do exactly this when your infrastructure is hosted in a Managed Cloud environment.
Other benefits of scaling out in a cloud environment include:
- Instant and continuous availability
- No limit to hardware capacity
- Cost can be tied to use
- You’re not stuck always paying for peak demand
- Built-in redundancy
- Easy to size and resize properly to your needs
How To Achieve Effective Horizontal Scaling
There are important best practices to keep in mind to make your service offering super compatible with horizontal scaling.
The first is to make your application stateless on the server side as much as possible. Any time your application has to rely on server-side tracking of what it’s doing at a given moment, that user session is tied inextricably to that particular server. If, on the other hand, all session-related specifics are stored browser-side, that session can be passed seamlessly across literally hundreds of servers. The ability to hand a single session (or thousands or millions of single sessions) across servers interchangeably is the very epitome of horizontal scaling.
The second goal to keep square in your sights is to develop your app with a service-oriented architecture. The more your app is comprised of self-contained but interacting logical blocks, the more you’ll be able to scale each of those blocks independently as your use load demands. Be sure to develop your app with independent web, application, caching and database tiers. This is critical for realizing cost savings – because without this microservice architecture, you’re going to have to scale up each component of your app to the demand levels of thservices tier getting hit the hardest.
No comments:
Post a Comment